Techno-Labo is a company which supports the development of plastic products by design, mechanical engineering, prototyping, and low volume production.
We propose our design with both drawings and prototyping. With a real prototype, you can see the shape, hold it by hand, review a fit with PCB so that you can get rid of your concern before mass-production starts.
Recently 3D drawings are hot tools, and we usually feel like beginning production immediately after creating drawings.
Hold on! You should check the real product with your hand.

In case you would feel wrong with the product, it’s too late after you made molds.
If you have the potential customers, why don’t you show them prototypes? They probably give you feedback to improve your products. If you exhibit your prototypes, you may hear unexpected requests or needs from visitors.
If you are about to order molds at the last minute before an exhibition or a presentation, there’s a better choice to make a prototype with a tiny cost.
A unit price of prototyping seems expensive. However, the cost range is from a few hundred dollars to a few thousand dollars. It is worth investing compared to the total development costs of a few ten thousand dollars.
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
< suitable qty: 1 to 5 >
The methods to form the 3D model using 3D-CAD data and a special device are called 3D printing. There are many types of 3D printers: SLA, SLS, FDM, ink-jet, and so on. All the methods form a cross-sectional layer of the model by curing liquid or powders partially, with a laminating pitch of 0.1 mm. Each method has merits and demerits of cost, speed, precision, toughness, and so on.
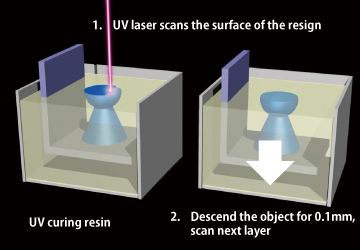
Basic process of SLA
There are many types of production methods which are called 3D printers.
3D Printing[Stereolithography (SLA) ]
It forms an object by hitting UV laser into the equipment that is filled with liquid epoxy resin. It requires the use of support structures to hold formed parts, which will leave marks when removed. If the design review needs a clean appearance, post-processing should be considered.
3D Printing[Selective laser sintering (SLS) ]
SLS forms an object by sintering powdered Nylon. Unlike SLA, SLS doesn’t require support structures because the powder won’t flow. SLS is useful to make hollow parts. The hard material is compatible with SLS and costs much lower than machining.
[ Machining ]
< suitable qty: 1 or 2 >
The machining center cuts a plastic block directly. Machining is compatible with the materials of real production and has a high-quality precision, so applicable to make movable products. However, it takes longer than other methods and costs high.
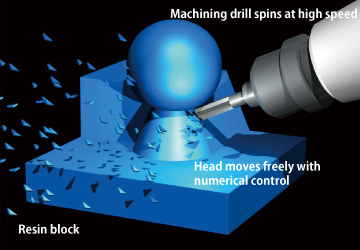
Basic process of Machining
[ Vacuum Casting (Copying Method) ]
< suitable qty: 5 or 20 >
It forms the object by adding and curing the liquid resin in the mold that is created by encasing the master model in liquid silicone rubber. It is often applied to make multiple copies of the master model, which is created with machining and SLA. It casts the resin in a vacuum to make a copy with high quality and no air bubbles.
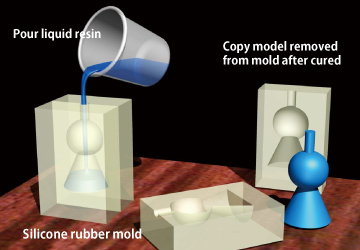
Basic process of Vacuum Casting